Fran
Administrator
AIMs: Interpret and calculate the variance for a portfolio and understand the derivation of the minimum variance hedge ratio.
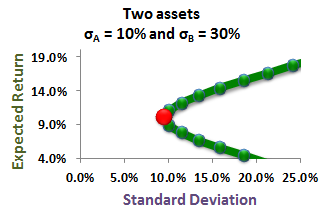
Questions:
305.1. A two-asset portfolio contains a long position in commodity (T) with volatility of 10.0% and a long position in stock (S) with volatility of 30.0%. The assets are uncorrelated: rho(T,S) = zero (0). What weight (0 to 100%) of the portfolio should be allocated to the commodity if the goal is a minimum variance portfolio (in percentage terms, as no dollars are introduced)?
a. 62.5%
b. 75.0%
c. 83.3%
d. 90.0%
305.2. A portfolio manager owns (has a long position in) $100 of Security A which has a volatility of 9.0%. She wants to hedge with Security B which has a volatility of 15.0%. The correlation between the securities is 0.40; rho(A,B) = +0.40. What position in Security B utilizes the minimum variance hedge ratio to create a portfolio with the minimum dollar ($) standard deviation?
a. Long $60.0
b. Short $24.0
c. Short $60.0
d. Short $76.0
305.3. A portfolio of $3.00 is equally invested in three securities (A, B and C), such that $1.00 is conveniently invested in each security, where the relationship between the securities is characterized by the following variance-covariance matrix:
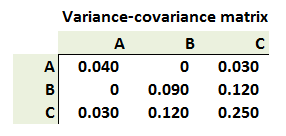
For example, the volatility of security A's returns is SQRT(0.040) = 20% and the covariance (B,C) = 0.120. What is the portfolio's dollar standard deviation?
a. $0.41
b. $0.55
c. $0.82
d. $1.34
Answers:

Questions:
305.1. A two-asset portfolio contains a long position in commodity (T) with volatility of 10.0% and a long position in stock (S) with volatility of 30.0%. The assets are uncorrelated: rho(T,S) = zero (0). What weight (0 to 100%) of the portfolio should be allocated to the commodity if the goal is a minimum variance portfolio (in percentage terms, as no dollars are introduced)?
a. 62.5%
b. 75.0%
c. 83.3%
d. 90.0%
305.2. A portfolio manager owns (has a long position in) $100 of Security A which has a volatility of 9.0%. She wants to hedge with Security B which has a volatility of 15.0%. The correlation between the securities is 0.40; rho(A,B) = +0.40. What position in Security B utilizes the minimum variance hedge ratio to create a portfolio with the minimum dollar ($) standard deviation?
a. Long $60.0
b. Short $24.0
c. Short $60.0
d. Short $76.0
305.3. A portfolio of $3.00 is equally invested in three securities (A, B and C), such that $1.00 is conveniently invested in each security, where the relationship between the securities is characterized by the following variance-covariance matrix:

For example, the volatility of security A's returns is SQRT(0.040) = 20% and the covariance (B,C) = 0.120. What is the portfolio's dollar standard deviation?
a. $0.41
b. $0.55
c. $0.82
d. $1.34
Answers:
